FRETbased Biosensor Visualizes Execution Of Necroptosis In Vivo
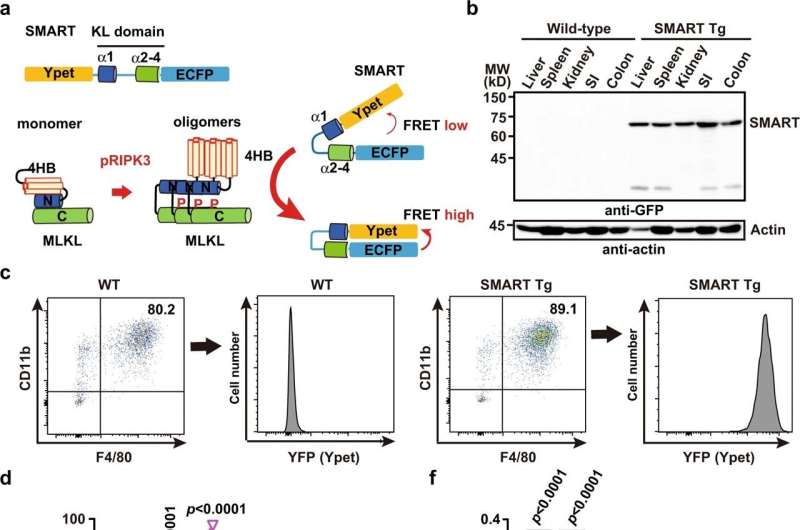
Necroptosis is apoptosis-like controlled cell death (RCD), the most studied type of RCD. In contrast to apoptosis, necroptosis occurs in cells with destruction of the plasma membrane. For this reason, scientists believe that necroptosis causes significant inflammation in surrounding tissue and plays a role in inflammatory disease. However, where and when necroptosis occurs under physiological and pathological conditions in vivo is not well understood.
Professor Dr. to solve this problem. Nakano's group developed a biosensor for necroptosis called SMART (FRET-based MLCL activation sensor of RIPK3). This biosensor is based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). In a 2018 Nature Communications article, they successfully identified necrosis in vitro using this FRET biosensor.
This time they have gone one step further. They developed intelligent transgenic mice with a FRET biosensor to monitor necroptosis in vivo. "The goal of our project is to study when and where necroptosis occurs in vivo and to understand its role in the pathological context," said Dr. Murray, lead author of the study.
In their experiments, they first confirmed that necroptosis can be regulated in primary macrophages or dead embryonic fibroblasts derived from SMART-Tg mice. They then applied a model of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury to SMART-Tg mice.
"After much trial and error, we were finally able to monitor necroptosis function in proximal tubular epithelial cells of SMART-Tg mice injected with cisplatin time, which effectively kills cells important in death control, using the two." alive," said the study's lead author, Professor Nakano.
“We believe that intelligent TG mice are a promising tool for imaging necrosis in vivo and will help to better understand the role of this newly discovered form of cell death, necroptosis, in disease pathophysiology.”
These findings have been published in the journal Communications Biology .
For more information: Shin Murai et al., Generation of Transgenic Mice Expressing a FRET Biosensor, Smart, Responsive to Necroptosis, Communication Biology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-04300-0
Provided by Toho University
Citation : FRET-based biosensor visual necroptosis in vivo (December 9, 2022) Retrieved December 15, 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-12-fret-based-biosensor-visualizes-necroptosis-vivo.html
This document is protected by copyright. No part may be reproduced without written permission, except for proper use for personal study or research. The content is provided for informational purposes only.








